wuf

OVERVIEW
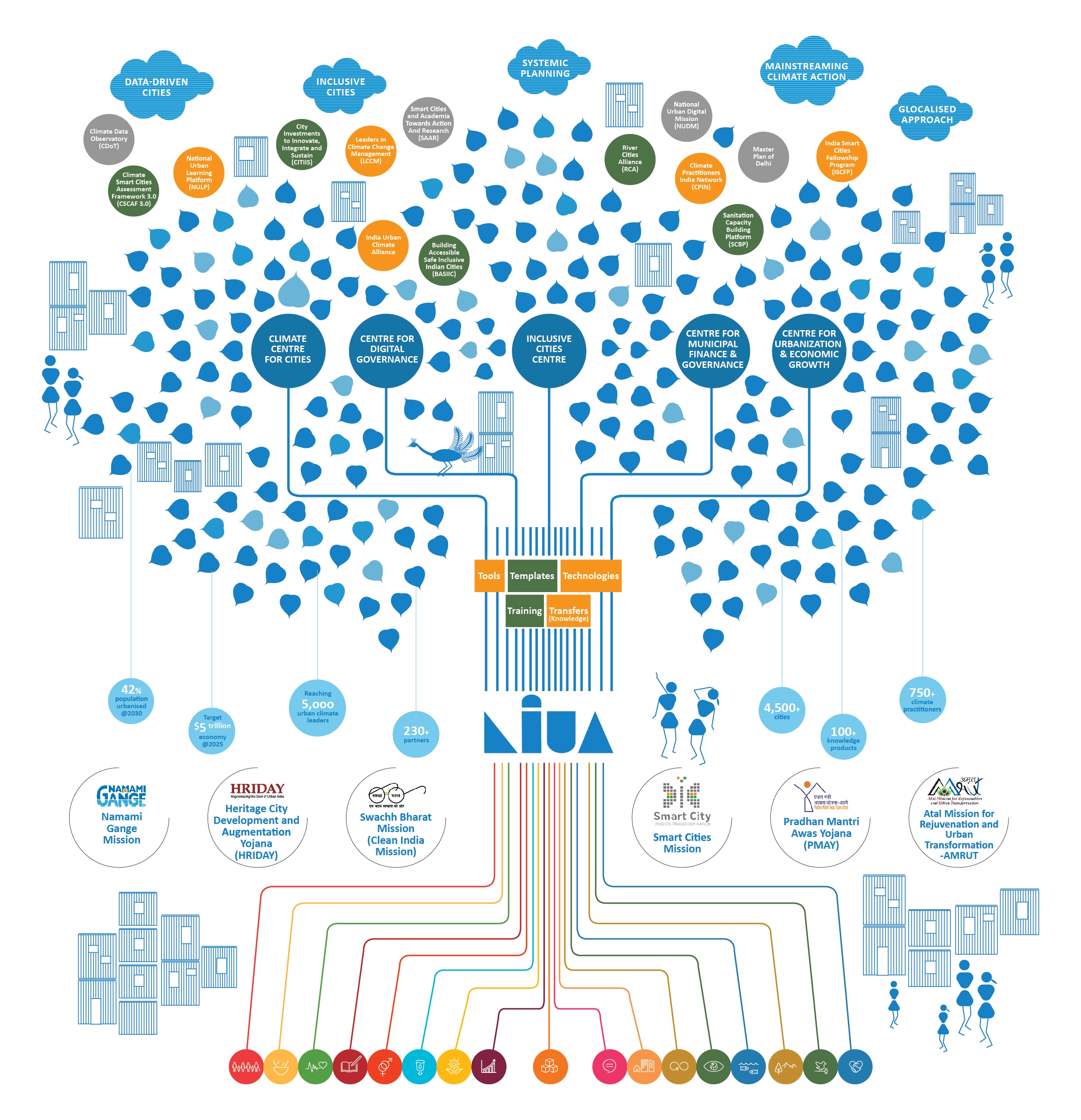
To foster partnerships, raise awareness and reinforce a common voice at the 12th session of WUF, the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA), Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), and Housing and Urban Development Corporation (HUDCO) intend to organise various sessi ons and activities that align with this year’s theme ‘It All Starts at Home’. NIUA, as the think tank of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in the Government of India, is planning to co-host the India pavilion to showcase the transformation of Indian cities through the perspectives of Research, Advocacy and Capacity.

EVENTS
Partner-led Events
05 November | 13:00-14:30
05 November | 13:00-14:30
Accelerating Inclusion and Resilience for all through Climate Finance and Participatory Actions in Cities. Partnerships for disability inclusion to leave no one behind.
Global Disability Innovation Hub (GDIH)
Climate Investments Funds, CBM Global, UN Habitat, NIUA, World Blind Union Click here
06 November | 13:00-14:30
06 November | 13:00-14:30
Bridging Divides - Residential Segregation in Asia and Africa
Shaanxi Normal University, China
"National Institute of Urban Affairs, India University of Glasgow, UK" Click here
06 November | 17:00-18:30
06 November | 17:00-18:30
Cities Leading The Way Combatting Plastic Pollution for a Sustainable and Circular Future
National Institute of Urban Affairs, India
UNEP, Paris Click here
07 November | 09:00-12:00
07 November | 09:00-12:00
Urban Solutions Lab: Interactive Games for Climate-Resilient and Livable Cities
AASTMT - Arab Academy for Science Technology and Maritime Transport, Egypt
"National Institute of Urban Affairs, India Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, India" Click here
07 November | 09:00-12:00
07 November | 09:00-12:00
Gender and Disability Inclusion in Urban Infrastructure- Accessibility Audit Toolkits for Urban Practitioners
United Nations in India
National Institute of Urban Affairs, India Click here
07 November | 13:00-14:30
07 November | 13:00-14:30
Empowering Local Climate Action- Governance, Data, and Contextual Insights from Cities in Asia and Africa
United Nations University, Bonn, Germany
"National Institute of Urban Affairs, IndiaGIZ India" Click here
07 November | 16:30-17:30
07 November | 16:30-17:30
Building Inclusive Cities - Innovative Pathways to Inclusion through Technology and Youth Engagement
National Institute of Urban Affairs, India
United Nations Resident Coordinator's Office (UNRCO) and citiesRISE NY Click here
India Pavilion Events
05 November | 10:00-10:45
05 November | 10:00-10:45
Title: Sustainable Urban Livelihoods: A Pathway to Inclusive Cities and Launch of the Centre for Sustainable Urban Livelihoods (CSUL)
Event Type: Launch
Organiser: MoHUA (PM SVAnidhi) & NIUA
05 November | 10:45-11:30
05 November | 10:45-11:30
Title: Round Table on Zero-waste Cities Alliance
Event Type: Launch
Organiser: NIUA, AIILSG, Sulabh International
05 November | 11:30-12:15
05 November | 11:30-12:15
Title: Pathways to Inclusion: Bringing Children into Policy and Planning
Event Type: Launch
Organiser: NIUA & UNICEF
05 November | 12:10-13:00
05 November | 12:10-13:00
Title: Integrating Nature-Based Solutions in Urban Planning
Event Type: Chat with Experts & Report Launch
Organiser: UN Habitat and Beyond Built Pvt. Ltd.
05 November | 14:00-14:45
05 November | 14:00-14:45
Title: Leading the Change - Local Solutions for Climate Change
Event Type: Lighting Talks
Organiser: NIUA & GIZ
06 November | 10:00-10:45
06 November | 10:00-10:45
Title: Digital Governance: Empowering Livelihoods through Technology and Innovation
Event Type: Case Clinic
Organiser: MoHUA & NIUA
06 November | 10:45-11:30
06 November | 10:45-11:30
Title: Sanitation Urban Game
Event Type: Board Game
Organiser: NIUA
06 November | 11:30-12:15
06 November | 11:30-12:15
Title: Urban Labs - scalable and data-driven digital solutions for promoting integrated, gender responsive, resilient, risk informed and sustainable urban development
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: GIZ, MoHUA, NIUA
06 November | 12:15-13:00
06 November | 12:15-13:00
Title: Meet the Mayors
Event Type: Meet the Mayor
Organiser: NIUA
06 November | 14:00-14:45
06 November | 14:00-14:45
Title: Digitalization, Emerging Technologies and Justice in Changing climate
Event Type: Case Clinic
Organiser: UNU-EHS, NIUA, ICLEI Africa & TERI
06 November | 14:45-15:30
06 November | 14:45-15:30
Title: Digital Public Infrastructure: Service Delivery and Capacity Building
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: NIUA & MoHUA
06 November | 15:30-16:15
06 November | 15:30-16:15
Title: Unpacking NBS: Stragtegies for Urban Resilience
Event Type: Pecha Kucha
Organiser: NIUA, India Forum for NBS
06 November | 16:15-17:00
06 November | 16:15-17:00
Title: Transforming Indian Cities - How Can Young Gamechangers Lead the Way?
Event Type: Youth Hour
Organiser: UN-Habitat & Fondation Botnar
07 November | 10:45-11:30
07 November | 10:45-11:30
Title: Enabling data-driven decision making for local governments: Spotlight on Open Data Initiatives in India and Germany
Organiser: GIZ, GMC, & ISCN
07 November | 12:15-13:00
07 November | 12:15-13:00
Title: Urban Innovation for Climate Action: Sub-National Climate Financing for Building Sustainable Cities
Event Type: Meet the Donor
Organiser: NIUA, AFD, KfW, GIZ
07 November | 14:00-14:45
07 November | 14:00-14:45
Title: Localised action for climate resilient and gender responsive urban infrastructure: From Policy to Practice
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: GIZ
07 November | 14:45-15:30
07 November | 14:45-15:30
Title: Fostering Sustainable Lifestyles through Climate-Smart Development and Urban Partnerships – Lessons from India
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: ICLEI, NIUA, GCOM, Swiss Embassy
07 November | 15:30-16:15
07 November | 15:30-16:15
Title: Accelerate Locally-Led Adaptation for Resilience Building in Cities
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: ICLEI, UNDRR, CDKN South Africa
08 November | 10:00-10:45
08 November | 10:00-10:45
Title: Designing Livable Cities: Enhancing Gender Inclusiveness and Accessibility for All
Event Type: Panel Discussion
Organiser: GIZ & MOHUA
08 November | 10:45-11:30
08 November | 10:45-11:30
Title: Financing Local Climate Action: Global Launch of the Enabling Framework Conditions Assessment Tools to Accelerate Urban Climate Finance.
Event Type: Launch
Organiser: UNESCAP, MoHUA, GIZ, NIUA, CCFLA & Govt of Indonesia

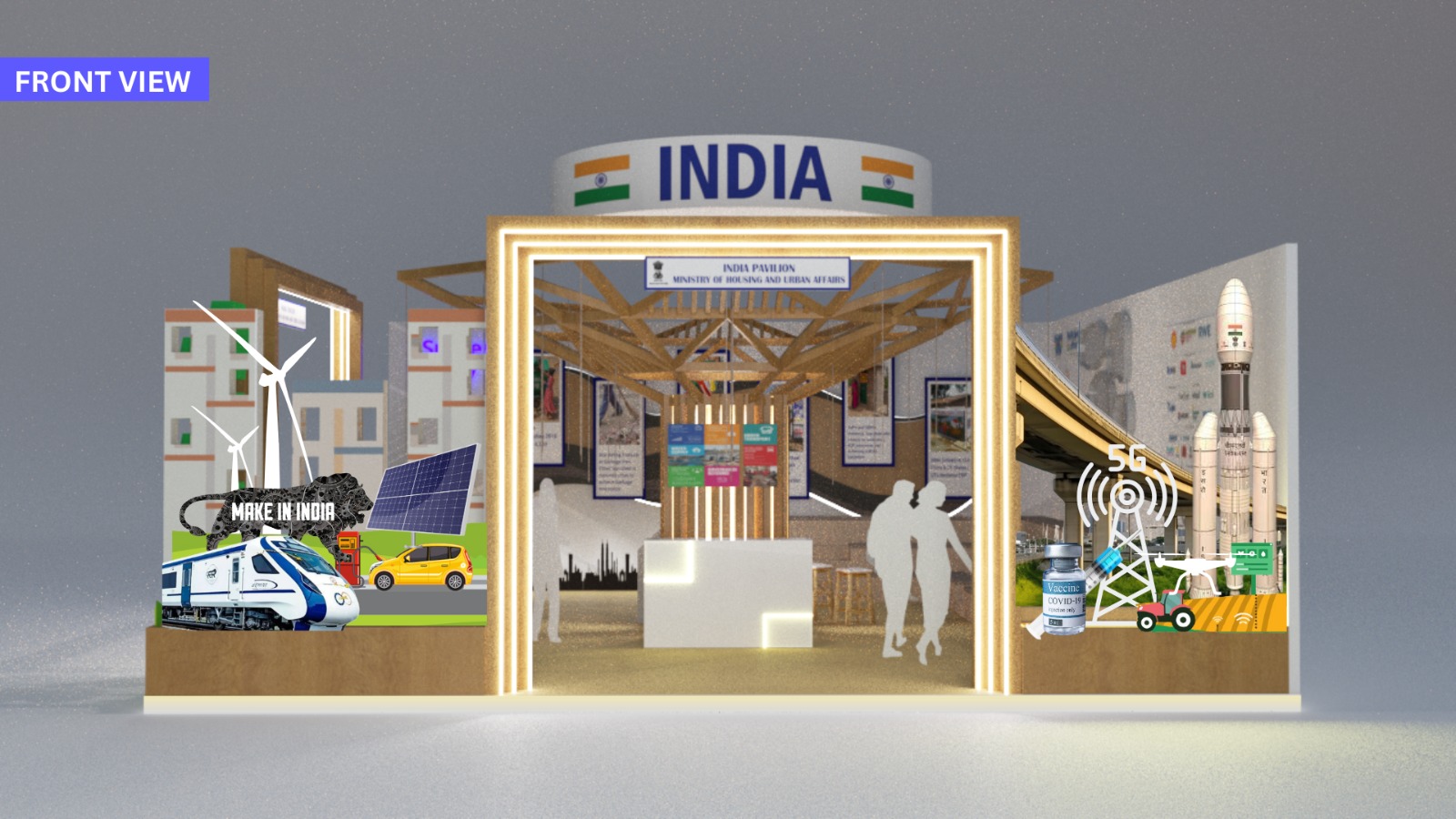
INDIA PAVILION
The India pavilion will serve as a platform for delegates worldwide to learn, discuss, visualise, and share what is happening in Indian cities. Additionally, it will help them understand how to communicate their impact more effectively to achieve scale and sustainability. The main objective is to demonstrate how India created an enabling ecosystem to influence multiple stakeholders in various ways to develop urban structures for the future. This approach can aid in effectively planning and managing urban challenges and ensure that Indian cities advance towards spatial, social, and economic inclusively. The exhibition will showcase India's endeavours in:
-
To inspire more cities to implement local initiatives and communicate the impact of their sustainable actions.
-
To garner more interest from cities and delegates in developing strategies for addressing future urban challenges.


SPEAKERS

Dr. Debolina Kundu
Director (AC), NIUA

Dr. Debjani Ghosh
Associate Professor, NIUA

Ms. Paramita Datta Dey
Head (Resources and Waste), NIUA

H.E. Mr. Taonga Mushayavanhu

Prof. Ya Ping Wang

Ms. Lina Liakou
Global Director, Resilient Cities Network, Netherlands

Dr. Tadashi Matsumoto
Head OECD

Dr. Himanshu Shekhar
UNU (Moderator), Germany

Dr. Remy Sietchiping

Mr. Andras Szorenyi

Ms. Shivani Gupta

Mr. Thomas George

Ms. Eider Inunciaga

Mr. Iain McKinnon

Ms. Zeina Elzein

Mr. Sandile Mbatha

Mr. Matt Hughsam

Mr. Sharon Gil

Ms. Mylene A. Rivera

Mr. Manjunath

Smt Kavita Padmanabhan

Ms. Nancy Abdel-Moneim

Dr. Umamaheshwaran Rajasekar
CDRI

Ms. Kanika Bansal
Lead- Universal Design and Inclusion, NIUA

Mr. Lovlesh Sharma
Sr. Water & Infrastructure specialist, NIUA

Manpreet Singh

Prerna Vijaykumar Mehta

Mr. Sarath Babu M G
Lead, Climate Centre for Cities, NIUA

Ms. Adishree Panda

Mr. Shantanu Padhi
Senior Program Officer - Technical, NIUA

Ms. Vaishnavi Shankar
Lead, NIUA

Mr. Utsav Choudhury
Team Leader, NIUA

Ms Deepshika Sinha
Program Associate, NIUA

Ms. Parul Agarwala
UN-HABITAT
Ms. Akruti Murhekar
Program Associate, NIUA (Presenter)

Mr. Vignesvar J
Project Associate, NIUA (Presenter)

Ms. Satarupa Roy
Program Associate, NIUA (Presenter)

PARTNERS






















