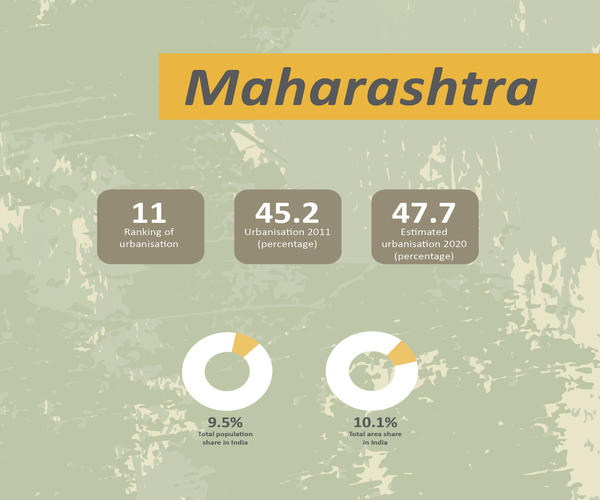
Today, just over half of the world’s population lives in urbanized areas. This share is expected to increase rapidly in coming decades, alongside rising incomes and a shift away from agriculture and rural economies. India, as a country making up one-sixth of the world’s population, is at the forefront of this change. Urban India is experiencing a major transformation. Urban population has experienced a six-fold increase since 1951, growing from 62.4 million to 377.1 million in 2011, and it is estimated that 590 million will live in Indian cities by 2030, which is twice the entire population of the USA. The challenge of Urbanisation and responsibilities of achieving the SDG 11 are imperative in India.
India's Urban Story is designed to enhance our understanding of the urban phenomenon, how it has unfolded itself in India and what directions it is setting for its future.

43.9
Total Populaton (Crore)
17.97
Urbanisation
2657
Number of Individual Towns
54.8
Total Populaton (Crore)
19.91
Urbanisation
3081
Number of Individual Towns
68.3
Total Populaton (Crore)
23.34
Urbanisation
3891
Number of Individual Towns
84.6
Total Populaton (Crore)
25.7
Urbanisation
4615
Number of Individual Towns
102.9
Total Populaton (Crore)
27.81
Urbanisation
5161
Number of Individual Towns
121
Total Populaton (Crore)
31.14
Urbanisation
7933
Number of Individual Towns
23.36%
Forest
9.03%
Non- Agricultural
5.51%
Barren and Unculturable
58.75%
Agriculturable
3.35%
Other

4624.2
ULBs per capita total Revenue
1975
ULBs per capita own revenue
688.2
ULBs per capita property tax
3569.9
ULBs per capita total expenditure
209
Municipal Corporation
2171
Municipal Councils
1879
Nagar Panchayat
2399.2
Average MPCE
0.36
Gini Coefficient for Urban consumption expenditure
13.7
Per Capita GSDP
45.8
Urban Worker population ratio (Percentage)
21.3
percentage of Urban Female workers in employment
20.79
percentage of urban workers in manufacturing
10.34
percentage of Urban Workers in Construction
142328
percentage of Urban Population living below Poverty Line (2011-12)
933
Sex Ratio
900
Urban Sex ratio
72.9
Litercay Rate
84.1
Urban Litercay rate
23
Under 5 mortality rate per 1000 live birth
80.01
Gross enrolment rate (secondary)
96.9
Gross enrolment rate (elementary)

India's Score on Relevant SDGs
47
SDG 2
74
SDG 3
83
SDG 6
92
SDG 7
79
SDG 9
74
SDG 11
74
SDG 12
54
SDG 13
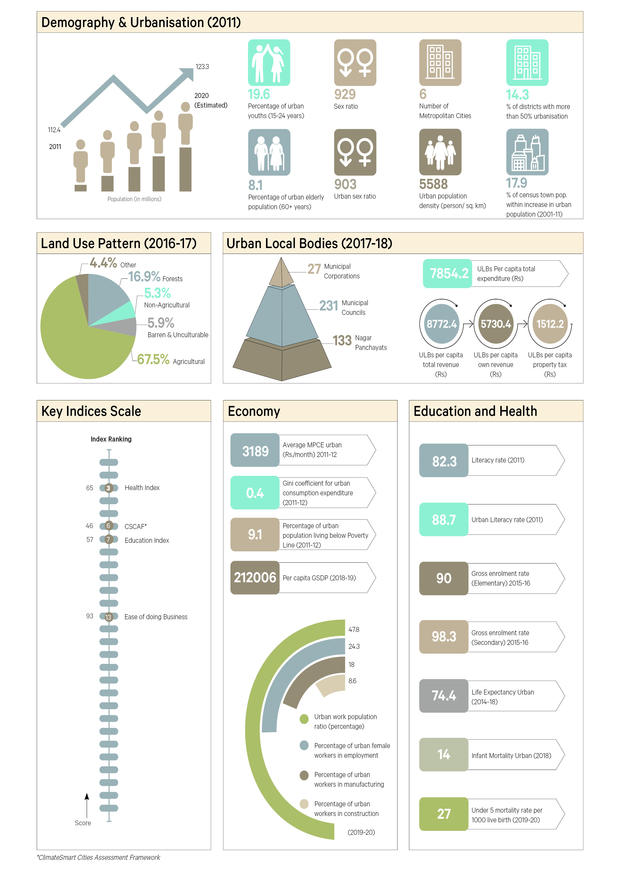
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2.LandUsePattern |
||||
16 |
Forests |
This includes all land classified either as forest under any legal enactment, or administered as forest, whether State- owned or private, and whether wooded or maintained as potential forest land. The area of crops raised in the forest and grazing lands or areas open for grazing within the forests remain included under the “forest area”. |
2016-17 |
LAND USE STATISTICS AT A GLANCE-State Wise, Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer Welfare |
17 |
Non-agricultural |
This includes all land occupied by buildings, roads and railways or under water, e.g. rivers and canals, and other land put to uses other than agriculture. |
2016-17 |
|
18 |
Barren & unculturable |
This includes all land covered by mountains, deserts, etc. Land, which cannot be brought under cultivation except at an exorbitant cost is classified as unculturable whether such land is in isolated blocks or within cultivated holdings. |
2016-17 |
|
19 |
Agricultural |
This includes Land under misc. tree crops & groves, Culturable waste land, Fallow Lands and Net Sown Area |
2016-17 |
|
20 |
Other |
Total geographical area subtracted by area covered under above categories (13-16) |
2016-17 |
|
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
3.UrbanLocalBodies |
||||
21 |
ULBs Per capita total revenue (Rs) |
ULBs Per capita total revenue is defined here as the ratio of total revenue generated by the ULB to its total population. |
2017-18 |
Ahluwalia, Isher Judge et. al (2019). State of Municipal Finances in India: A Study Prepared for the Fifteenth Finance Commission, ICRIER, New Delhi. |
22 |
ULBs Per capita own revenue (Rs) |
ULBs Per capita own revenue is defined here as the ratio of total own revenue generated by the ULB to its total population. |
2017-18 |
|
23 |
ULBs Per capita property tax (Rs) |
ULBs Per capita property tax is defined here as the ratio of total property tax collected by the ULB to its total population. (Property tax is a part of own revenue) |
2017-18 |
|
24 |
ULBs Per capita total expenditure (Rs) |
ULBs Per capita total expenditure is defined here as the ratio of total expenditure done by the ULB to its total population. |
2017-18 |
|
25 |
Municipal Corporations (top) |
A Municipal Corporation is constituted for a larger urban area |
2011 |
|
26 |
Municipal Councils (middle) |
A Municipal Council is constituted for a smaller urban area |
2011 |
|
27 |
Nagar Panchayats (last) |
Nagar Panchayat for a transitional area, that is to say, is an area in transition from a rural area to an urban area. |
2011 |
|
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4.Economy |
||||
28 |
Average MPCE urban (Rs./ month) |
The NSS concept of MPCE is defined first at the household level (household monthly consumer expenditure ÷ household size). This measure serves as the indicator of the household’s level of living. |
2011-12 |
National Sample Survey Organization, 68th round. |
29 |
Gini coefficient for urban consumption expenditure |
The Gini coefficient is a single number that demonstrates a degree of inequality in a distribution of income/wealth. It is used to estimate how far a country’s wealth or income distribution deviates from a totally equal distribution. , 0 corresponds to perfect income equality and 1 corresponds to perfect income inequality |
2011-12 |
National Sample Survey Organization, 68th round. |
30 |
Percentage of Urban Population Living below poverty line consumption expenditure |
Population living below poverty line |
2011 |
Tendukar Commitee 2011-12 |
31 |
Per capita GSDP |
Gross State Domestic Product divided by Population |
2018-19 |
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation |
32 |
Urban worker population ratio (percentage) |
Worker Population Ratio (WPR): WPR defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population. Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS) figure adopted for the persons of age15 years and above |
2018-19 |
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) |
33 |
Percentage of urban Female workers in employment | 2018-19 |
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) |
|
34 |
Percentage of urban workers in manufacturing |
Number of urban workers in the Manufacturing sector divided by employed persons in the population |
2018-19 |
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) |
35 |
Percentage of urban workers in construction |
Number of urban workers in the construction sector divided by employed persons in the population. |
2018-19 |
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) |
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
5.KeyIndicesScale |
||||
36 |
Education Index |
School Education Quality Index –
the school education sector. It seeks to institutionalise a focus on enhancing education outcomes by driving improvements in learning levels, access, equity, infrastructure and governance processes.
|
|
NITI Aayog |
37 |
Health Index |
The index aims to nudge States towards transformative action in the health sector. NITI Aayog is committed to establishing the health index as an annual systematic tool to focus the attention of the States/UTs on achieving better health outcomes.
| 2017-18 | NITI Aayog |
38 |
Ease of Doing Business |
The Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index is a ranking system established by the World Bank Group. In the EoDB index, ‘higher rankings’ (a lower numerical value) indicate better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights. |
NITI Aayog.(2020). India Voluntary National Review 2020:Decade of Actions Taking SDGs from Global to Local. NITI Aayog |
|
39 |
CSCAF |
Refer Point 12 for details. |
||
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6.EducationandHealth |
||||
40 |
State literacy rate |
A person aged seven and above who can both read and write with understanding in any language, is treated as literate. |
2011 |
Handbook of Statistics in India, RBI |
41 |
Urban litercay rate |
Literacy rate of the Urban Area in the State. |
2011 |
Handbook of Urban Statistics 2016, MoHUA |
42 |
Gross enrolment rate (secondary) |
Total enrolment in a specific level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the eligible official school-age population corresponding to the same level of education in a given school-year. |
2015-16 |
Ministry of Human Resource Development.(2018). Educational Statistics at a Glance, Ministry of Human Resource Development, Department of School Education and Literacy, Govt. of India, New Delhi. |
43 |
Gross enrolment rate (elementary) |
Total enrolment in a specific level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the eligible official school-age population corresponding to the same level of education in a given school-year. |
2015-16 |
Ministry of Human Resource Development.(2018). Educational Statistics at a Glance, Ministry of Human Resource Development, Department of School Education and Literacy, Govt. of India, New Delhi. |
44 |
Life expectancy Urban |
Life expectancy usualy measure the average number of years a persons is expected to live under prevalling mortality condition |
2014-18 |
SRS, Statistical Report, Census of India |
45 |
Infant Mortality Urban |
Infant Mortality rate is defined as the infant deaths (less than one year) per thousand live births. |
2018 |
SRS, Statistical Report, Census of India |
46 |
Under 5 mortality rate per 1000 live birth |
The probability of a child born in a specific year or period dying before reaching the age of five. |
2019-20 |
International Institute for Population Studies.(2021). National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) India, IIPS, Mumbai. http://rchiips.org/nfhs/factsheet_NFHS-5.shtml |
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
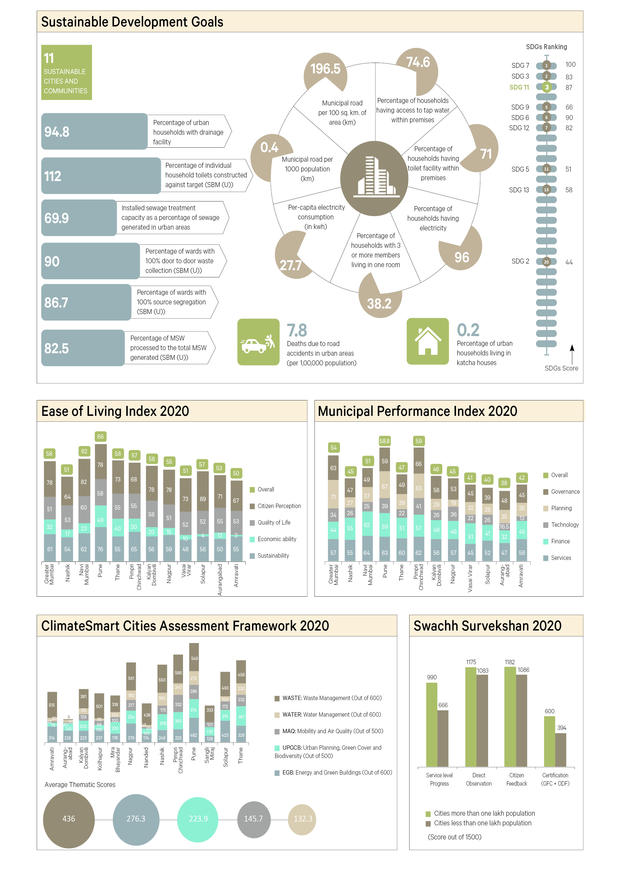
7.SustainableDevelopmentGoals |
||||
47 |
Percentage of urban households living in katcha houses |
This target corresponds to the global SDG target 11.1 that aims to ensure universal access to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services, and upgrade slums, by 2030. |
2018 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
48 |
Percentage of urban households with drainage facility |
This target corresponds to the global SDG target 11.1 that aims to ensure universal access to basic services |
2018 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
49 |
Percentage of individual household toilets constructed against target (SBM(U)) |
Swachh Bharat Mission aims to provide universal sanitation coverage in urban areas through construction of IHHL units and community toilets. It aims for completion of construction of toilets targeted and sanctioned. |
2020 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
50 |
Deaths due to road accidents in urban areas (per 1,00,000 population) |
This target corresponds to the global SDG target 11.2 that focuses on improving road safety, and also the global SDG target 3.6 which aims to halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents. |
2019 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
51 |
Percentage of wards with 100% door to door waste collection (SBM(U)) |
Swachh Bharat Mission in urban areas aims to operationalise 100 percent door to door collection of waste in all wards |
2020 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
52 |
Percentage of MSW processed to the total MSW generated (SBM(U)) |
This target corresponds to the global SDG target 11.6 that aims to reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities by 2030, by focusing on municipal and other waste management. MSW processing is also critical to the success of the SBM (U). |
2020 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi. https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
53 |
Percentage of wards with 100% source segregation (SBM(U)) |
Swachh Bharat Mission in urban areas aims to operationalise 100 percent segregation of waste in all wards |
2020 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi.https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
54 |
Installed sewage treatment capacity as a percentage of sewage generated in urban areas |
This target corresponds to the global SDG target 11.6 that aims to reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities by 2030, by focusing on waste management. |
2018 |
NITI Aayog.(2021). SDG India Index & Dashboard 2020-21: Partnerships in the Decade of Actions, NITI Aayog, Govt. of India, New Delhi.https://niti.gov. in/writereaddata/files/SDG_3.0_ Final_04.03.2021_Web_Spreads. pdf |
55 |
Percentage of households having access to tap water within premises |
The study conducted on Cities and the Sustainable Development Goal 11 indentified these indicators to evaluate the performace of SDG 11. |
Study on Cities and the Sustainable Development Goal 11 |
|
56 |
Percentage of households having latrine facility within premises |
|||
57 |
Percentage of households having electricity |
|||
58 |
Percentage of households with 3 or more members living in one room |
|||
59 |
Per-capita electricity consumption (in kwh) |
|||
60 |
Municipal road per 1000 population (km) |
|||
61 | Municipal road per 100 sq. km. of area (km) |
|||
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8.SDG Performance Scale |
||||
62 |
SDG 2 |
The composite index is the arithmetic mean of the Goal Score for 16 Goals, for each state/UT, assigning equal weights to each Goal. This score is an indication of the overall position of state/UTs in their journey towards achieving SDGs. |
2020 |
https://sdgindiaindex.niti.gov.in/#/ ranking |
63 |
SDG 3 |
|||
64 | SDG 5 |
|||
65 | SDG 6 | |||
66 |
SDG 7 | |||
67 | SDG 9 | |||
68 | SDG 11 | |||
|
69 |
SDG 12 |
|||
70 |
SDG 13 |
|||
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
10. Ease of Living Index |
||||
71 |
Sustainability |
Sustainability, along the lines of availability of green spaces, promotion of green buildings, level of energy consumption, the quality of natural resources such as air and water, and the city’s ability to withstand natural disasters. It holds a weightage of 20% in the final index score. |
2020 |
Institute for Competitiveness. (2021). Ease of Living Index 2020, IFC, New Delhi |
72 |
Economic ability |
Economic Ability captures the economic well-being of citizens by evaluating the level of economic development and inequalities that they encounter in a particular city. This pillar holds a weightage of 15% in the final index score. |
2020 |
|
73 |
Quality of Life |
Quality of Life uncovers an understanding of the different aspects contributing to a decent urban life. By examining provisions for necessities such as affordable housing, access to clean water, basic education, healthcare facilities, safety and security, and recreation avenue, the goal has been to assess a holistic impression of the quality of life in India’s urban cities. It holds a weightage of 35% in the final index score. |
2020 |
|
74 |
Citizen perception |
The Citizen Perception Survey (CPS) provides a perception of the city residents and allows them to evaluate the level and quality of development in their respective cities. Furthermore, the survey acts as a source to validate the findings of the index and examine whether they comply with the results of the data provided by the cities. The CPS pillar holds a weightage of 30% in the overall index score. |
2020 |
|
75 |
Overall |
The Ease of Living Index 2020 presents itself as an evaluation tool that reflects the ease of living in Indian cities. It seeks to examine the impact of urban development programs and the quality of life and economic and social opportunities available to the citizens. It measures the ease of living across four pillars: Quality of Life, Economic Ability, Sustainability, and Citizen Perception. |
2020 |
|
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
11. Municipal Performance Index |
||||
76 |
Services |
Services include an assessment of all functions that citizens experience on a daily basis such as education, health, water and wastewater, SWM and sanitation, registeration and permits, and infrastructure. |
2020 | Institute for Competitiveness. (2021). Municipal Performance Index 2020, IFC, New Delhi |
77 |
Finance |
Finance measures municipalities based on how they manage public funds and how their agency is accessing financial resources such as revenue management, expenditure management, fiscal responsibility, and fiscal decentraization. |
2020 |
|
78 |
Technology |
Digital coverage of municipality services and the extent to which it empowers its citizens to access such services, is measured under Technology. This includes digital governance, digital access, digital literacy. |
2020 |
|
79 |
Planning |
Planning examines the level of preparation, implementation, and enforcement of urban planning such as plan preparation, implementation and enforcement. |
2020 |
|
80 |
Governance |
Governance deals with aspects of municipal bodies and their governance mechanism such as transparency and accountability, human resources, participation, and effectiveness. |
2020 |
|
81 |
Overall |
The Municipal Performance Index assesses the sectoral/sectors performance of municipalities, serving as a guide for informed policy decisions, and helping achieve broader development outcomes and the Sustainable Development Goals across cities. |
2020 |
|
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
12. ClimateSmart Cities Assessment Framework | ||||
82 |
Energy and Green Buildings |
ClimateSmart means anchoring of climate actions within activities catering to urban development. This includes municipal services such as water supply and solid waste management, but also infrastructure projects such as housing, planning and land development, etc. Climate smart development responds to the changing climatic conditions and fistering sustainable actions which could help in increasing the ease of living within cities. The ClimateSmart Cities Assessment Framework 2.0 is broadly categorised into 5 sectors with 28 indicators (Table 2). Weightage:
|
2020 |
Climate Centre for Cities, National Institute of Urban Affairs |
83 |
Urban Planning, Green Cover and Biodiversity |
|||
84 |
Mobility and Air Quality |
|||
85 |
Water Management |
|||
86 |
Waste Management |
|||
| S. No. | Indicator | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
13. Swachh Survekshan |
||||
87 |
Service level progress |
The Swachh Survekshan (2020), was conducted to study the progress of Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban) and rank Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India based-on cleanliness and sanitation parameters. The Survekshan has evaluated 4242 cities in 2020. |
2020 |
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.(2020). Swachh Survekshan 2020, Government of India, New Delhi. |
88 |
Direct observation |
|||
89 |
Citizen feedback |
|||
90 |
Certification (GFC + ODF) |
|||